Measuring ROI – Assessing the Value of Data Lineage
Data lineage has become a significant aspect of data governance, serving as the backbone for understanding, managing, and safeguarding the journey of data. With discussing data lineage, assessing the impact and value of the tools that make it possible is important. This article will look at data lineage, its importance, and the methodologies to evaluate its tools.
Table of Contents
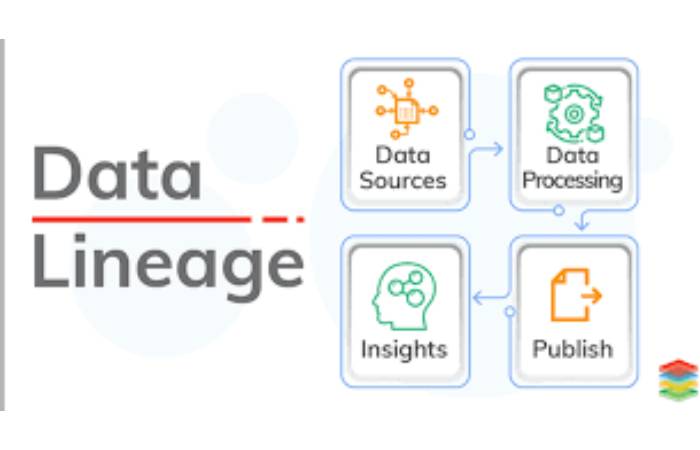
What is Data Lineage?
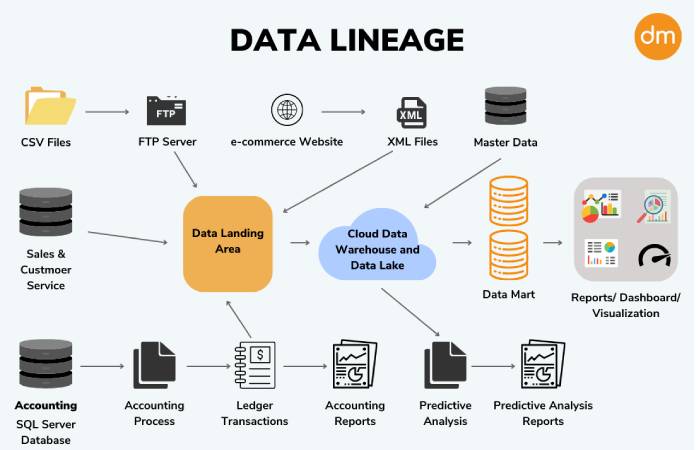
Data lineage, also known as data provenance or data tracing, is the process of tracking data as it moves within an organization to understand its origins, the ways it’s been modified, as well as who is using it and how.
This process highlights the origins, alterations, and impacts of data, offering profound insights into its lifecycle. Understanding data lineage is akin to unraveling the story of your data – where it comes from, how it morphs, and its implications on business outcomes.
Why is Data Lineage important?
Enhanced Data Quality: Data lineage helps organizations identify and fix issues relating to data quality. Due to data lineage enabling the discovery of the data path, it is easier to pinpoint discrepancies, errors, or inconsistencies in any given data set. This allows for better decision making with data management.
Ensuring Compliance: Data lineage allows organizations to display accuracy and security with their data. This is more critical for organizations within the finance and healthcare sectors which have to be compliant with several data regulations and standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO.
Documenting data provenance and consent through data lineage aids in complying with stringent data regulations and standards like GDPR. This not only mitigates legal risks but also fosters a culture of transparency and accountability.
Boosting Data Security: Poor data quality and regulatory non-compliance pose significant financial and reputational risks to organizations. Data lineage helps mitigate this by proactively monitoring data access and usage, detecting and recording breaches, and maintaining a vigilant eye on data anomalies.
This summates to a robust data security policy thereby helping in safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access or malicious activities.
Maximizing Data Value: Data lineage helps enhance data value by enabling data discovery, fostering reuse, and promoting collaboration. By understanding how data contributes to business objectives, organizations can extract maximum value from their data assets.
Enhances scalability: Data lineage creates a base for allowing organizations to understand how data flows through their systems. This is particularly useful when organizations look to scale. Data lineage offers that needed insight into how organizations can effectively evolve while also maintaining efficient, cost-effective, and scalable data management practices.
Metrics for Assessing Data Lineage Impact
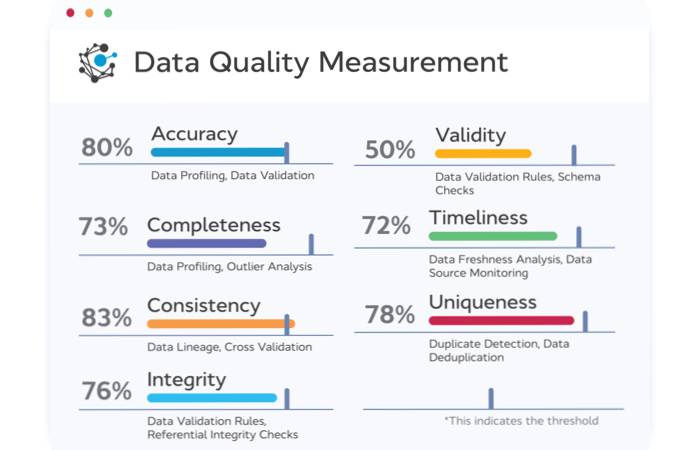
To gauge the impact of data lineage tools, a strategic approach is essential. One that aligns data governance goals with business objectives is the initial step, followed closely by tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) over time. These KPIs include:
Data Accuracy: This assesses the precision of data representations, ensuring that decisions and insights derived from the data are reliable, leading to increased trust in the data.
Data Completeness: This evaluates the comprehensiveness of data records and ensures that the entire scope of information is considered, preventing oversight or incomplete analyses.
Data Timeliness: This ensures that data is available within the required time frames. This is crucial for scenarios where real-time insights or operational efficiency is paramount.
Data Availability: This confirms the accessibility of data when needed ensuring that the data is a valuable and reliable resource for all relevant stakeholders.
Compliance Rate: This KPI measures adherence to data regulations, Helping organizations build a strong regulatory posture, mitigating legal risks, and earning the trust of customers and partners.
Security Incidents: Monitoring and mitigating data security breaches ensures the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information, safeguarding the organization’s reputation.
Data ROI: Calculating the return on investment derived from data-related initiatives provides a tangible measure of the value generated through effective data governance.
Quantifying the Value of Data Lineage Tools
Estimating the value of data lineage tools involves a meticulous consideration of costs and benefits. The costing encompasses initial investments, maintenance, operational expenses, user training, and support. On the flip side, benefits include savings and revenues generated by improving data quality, compliance, security, and overall value. Employing methods like cost-benefit analysis (CBA) or return on investment (ROI) aids in selecting tools that offer optimal value.
Selecting the right Data Lineage Tool
When selecting the right data lineage tool, it is important to consider the following factors:
Data Characteristics: How the tool characterizes data is important, particularly how it reflects on the nature of the data – its sources, formats, volumes, and flows. This ensures that the selected tool aligns with the intricacies of your data landscape.
Governance Framework: The data lineage tool you select should align with your data governance framework, encompassing policies and roles. A tool that aligns with governance structures ensures seamless integration into existing processes.
Tool Features: Generally, it is important to evaluate any software based on its features, functionalities, and integrations. When selecting a data lineage tool, this should not be any different. The chosen tool should offer a comprehensive suite of features that address the specific needs of your organization.
Use Cases and Scenarios: The data lineage tool selected should have a diverse range of use cases for better integration. Organizations should select a data lineage tool with specific use cases and scenarios pertinent to the organizational needs. A tool that caters to diverse use cases ensures versatility in application.
Requirements: Organizations need to tailor their choice of data lineage software based on their data lineage requirements. Identifying and prioritizing specific requirements ensures a more tailored and effective implementation.
Using tools like a data lineage tool comparison matrix or an evaluation checklist streamlines the selection process, ensuring better alignment with organizational objectives.
Best Practices for Utilizing Data Lineage Tools
Effectively utilizing a data lineage tool involves adhering to certain best practices. These are:
Define Scope and Granularity: Clearly outline the scope and granularity of your data lineage. This ensures that the tool focuses on the most critical aspects of your data landscape.
Mapping: Map data sources, transformations, and destinations comprehensively. A detailed mapping provides a holistic view of how data moves within the organization.
Documentation: Document metadata and annotations associated with data lineage. Comprehensive documentation enhances the interpretability of data lineage, aiding in understanding and decision-making.
Visualization: Leverage visualization techniques to represent data lineage flows and dependencies. Visual aids simplify complex data relationships, making them accessible to a broader audience.
Analysis: Analyze insights and impacts derived from data lineage. Regular analysis ensures that data governance policies remain aligned with evolving business needs.
Monitoring: Implement monitoring mechanisms to track changes and receive alerts. Proactive monitoring helps in addressing issues before they escalate, ensuring the ongoing reliability of data.
Integration with Governance regulations: Extend the use of data lineage tools to support other data governance regulations, including quality assessment, compliance audits, security reviews, and value optimization.
Conclusion
In an era where data is a strategic asset and the very lifeblood of organizations, effectively managing it is essential for organizational success. Data lineage emerges as a powerful tool for doing just that, providing transparency, enhancing data quality, and supporting regulatory compliance.
The ROI of data lineage goes beyond financial, it also helps with strategic decision making, risk mitigation, and scalability. While challenges would exist, the long-term benefits far outweigh the investments, making data lineage a valuable asset to organizations in this data-driven digital ecosystem.

